Scientific Research
Prof. Dinov conducts research in computational
and data science, artificial intelligence and statistical learning, health analytics,
neuroscience and brain mapping, mathematical modeling, statistical inference, bioinformatics,
and STEM education.
Publications »
Patents »
Grants »
Computational and Data Science, Predictive Analytics
There are a number of challenges, opportunities, and strategies for designing, collecting, managing, processing, interrogating, analyzing and interpreting complex datasets. We develop, validate and share methods, software tools, and protocols that can be applied to a broad spectrum of Big Data problems. This includes building mathematical foundations, computational statistics algorithms, and modern scientific inference techniques to model, visualize and interpret heterogeneous biomedical data. DSPA »
Neuroscience and Brain Mapping
We are involved in challenging neuroscience projects examining brain development, maturation and aging in health and disease. Specific projects include studying normal and pathological pediatric development (e.g., Autism, ADHD, Schizophrenia), memory decline and dementia (e.g., Alzheimer's disease), and various other brain related disorders (e.g., ALS, Parkinson's disease).
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
We develop meta-algorithms for data harmonization, aggregation, model-based and model-free inference (e.g., SOCR AI Bot, see AI Bot video 1 and AI Bot video 2, CBDA, DataSifter).
STEM education
We develop interactive learning modules, dynamic instructional resources, and technology-enhanced educational resources (e.g., MIDAS Graduate Data Science Certificate Program, Graduate Health Analytics Curriculum). Prob & Stats EBook » SMHS EBook »
Computational Medicine and Bioinformatics
Integration of cognitive, genetics, phenotypic, imaging, and biospecimen data requires novel strategies to represent high-dimensional and incongruent data as computable data objects. This research project aims to develop effective informatics techniques that address this difficult challenge using a scalable, reproducible, and reliable computational workflow environment (e.g., Pipeline workflows).
Spacekime Analytics
We are developing a novel theoretical foundation to extend the notion of time to the complex plane. This approach lifts the concept of time from a positive real number representing event ordering to a 2D complex-time (kime) comprising a pair of coordinates - time (t) and phase (φ). Spacekime analytics enables powerful data-driven strategies to interrogate large longitudinal data. This fundamentals research project explores time-complexity and inferential uncertainty in modeling, analyzing, and interpreting large, heterogeneous, multi-source, multi-scale, incomplete, incongruent, and longitudinal data.
Spacekime »Multidisciplinary Design Projects (MDP)
SOCR MDP R&D projects and other specific ongoing student, fellow, and scholar science and discovery projects are openly shared and disseminated.
Shape Modeling
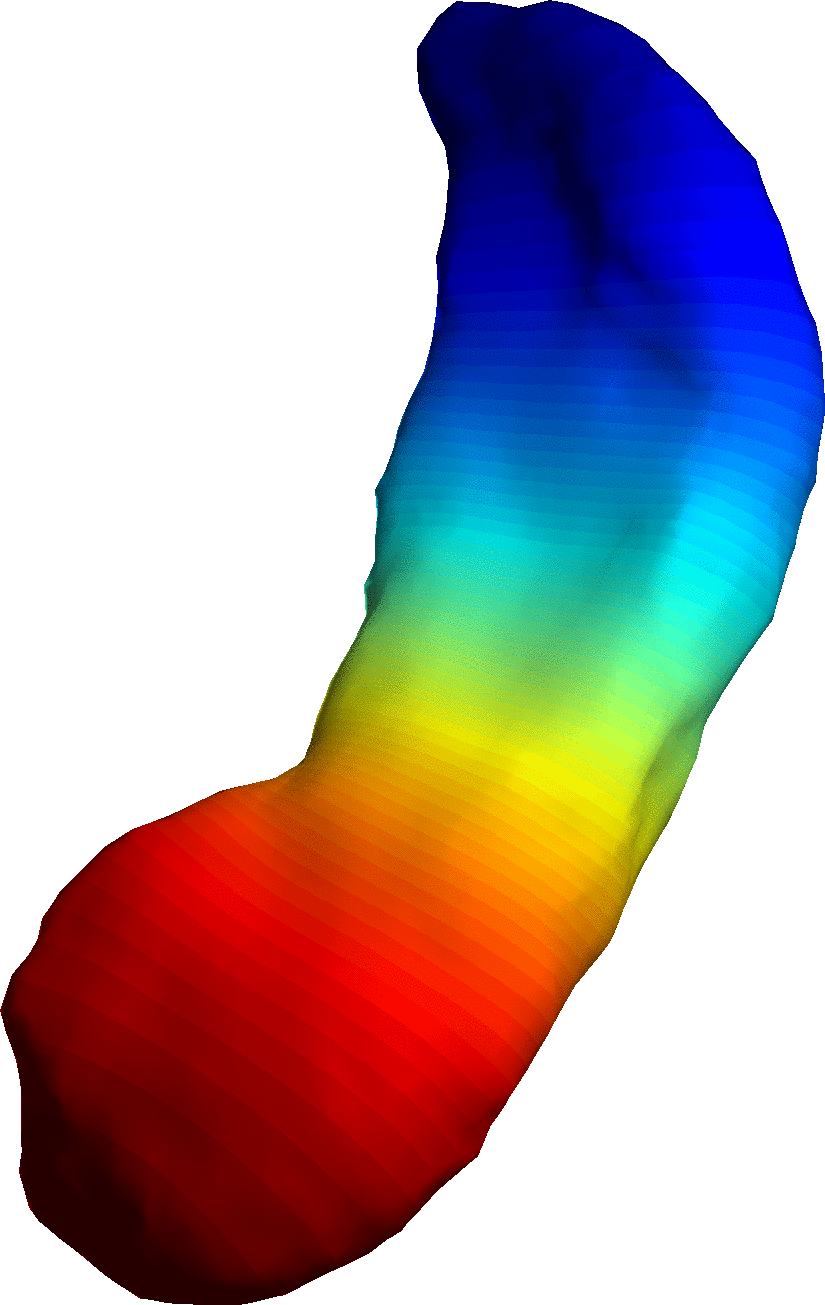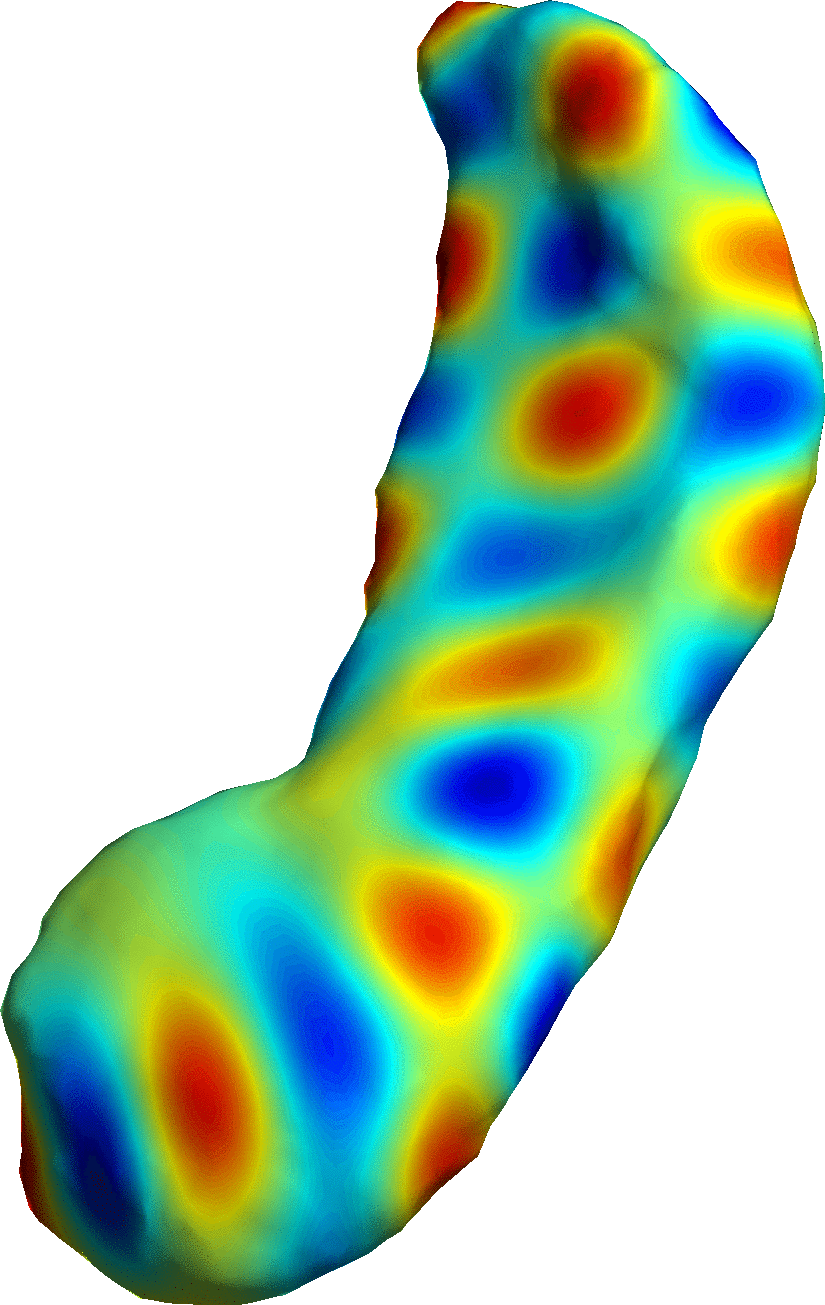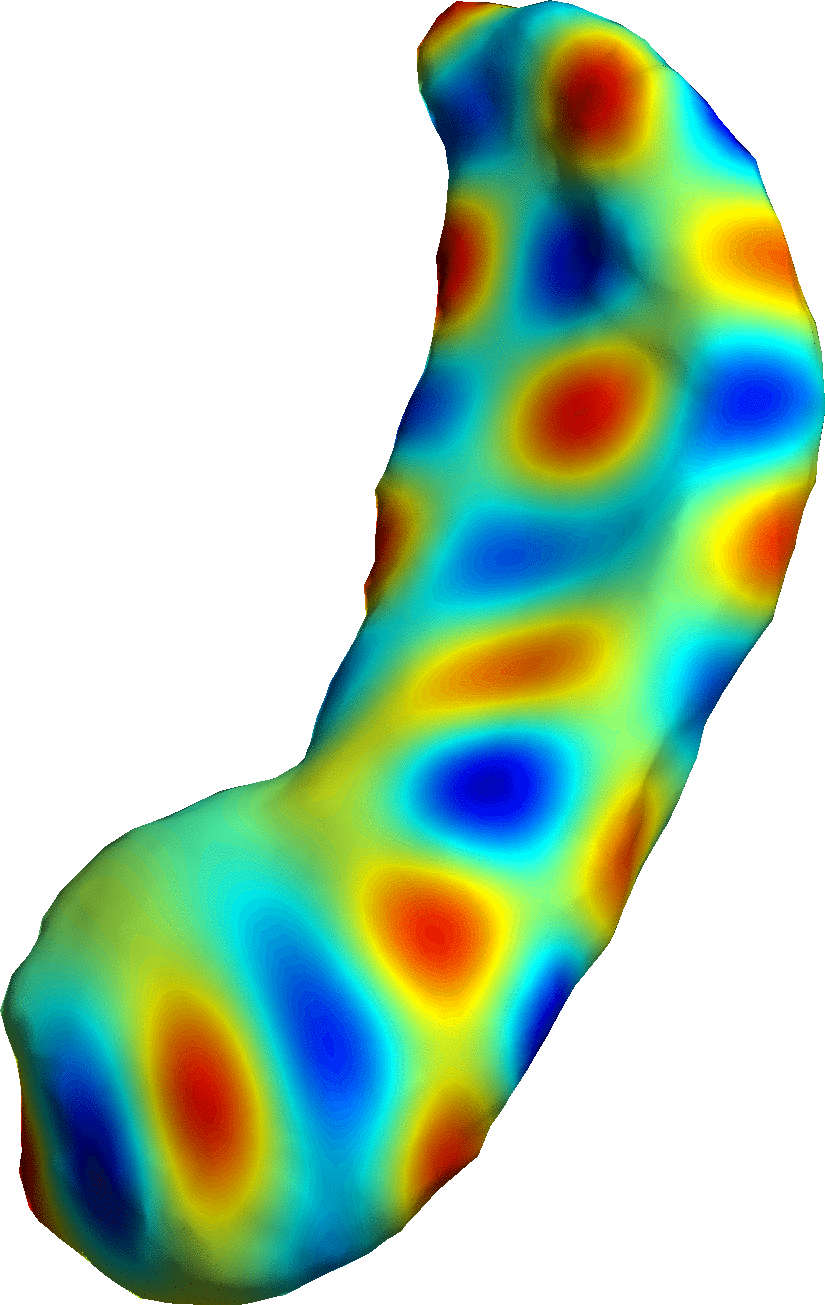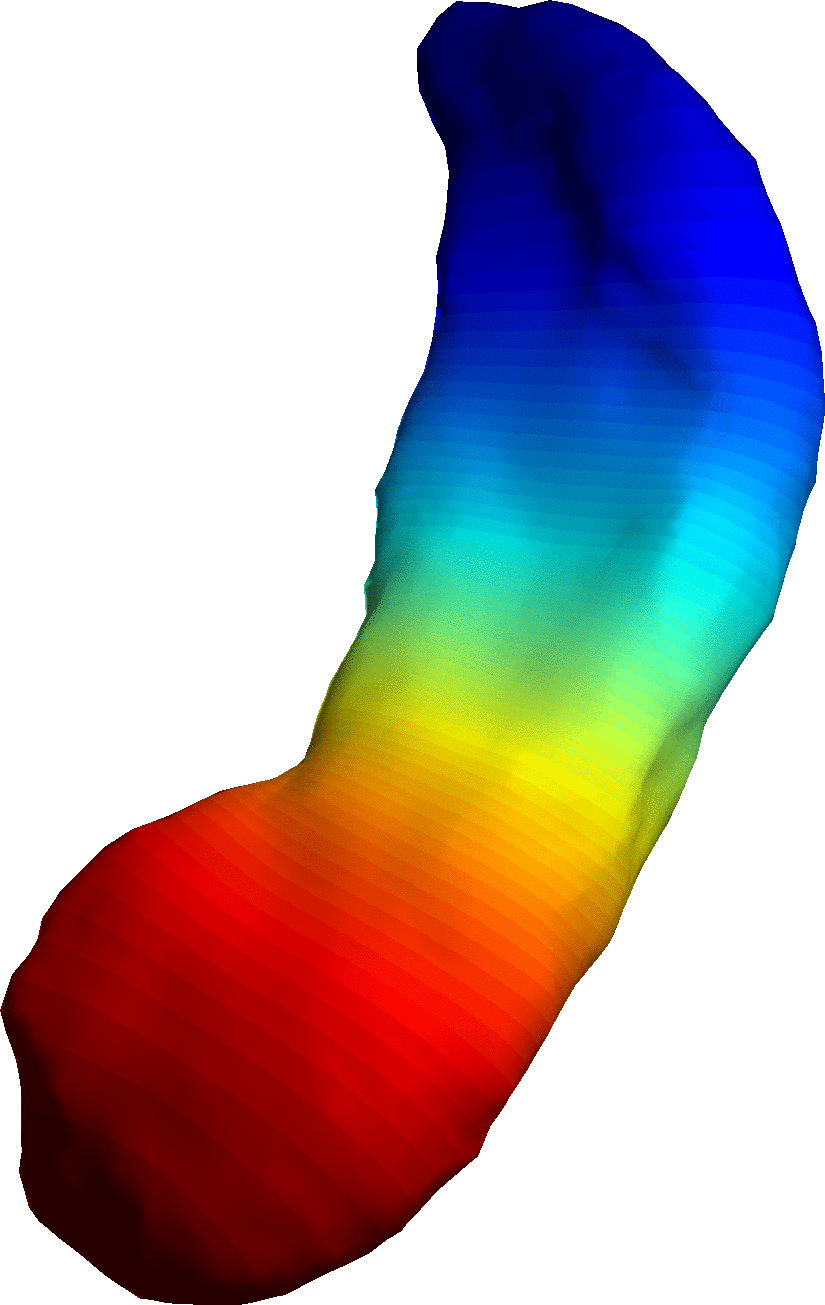 Modeling of Biological Shape Form and Size.
This project introduces and evaluates effective, robust and
efficient techniques for representation of N-D signals in
non-Euclidian spaces (e.g., cortical surfaces, nuclear
envelopes, nucleoli shapes, etc.
Modeling of Biological Shape Form and Size.
This project introduces and evaluates effective, robust and
efficient techniques for representation of N-D signals in
non-Euclidian spaces (e.g., cortical surfaces, nuclear
envelopes, nucleoli shapes, etc.
Open-Science
Develop, validate, support, and share an open access sustainable framework for data management, computational infrastructure, analytical tools, learning resources, and web-services. There have been a total of over 16 Million users (2020) of these open-science resources.
| Resource Type | Description | Examples |
| Data Web-services Annual Users:15,000 |
Research-derived, simulated, translational and clinical data archives. Dashboard for mashing multi-source socioeconomic and medical datasets, big data analytics, graphical data exploration and discovery | UMich
SOCR Data UCLA SOCR Data Archive SOCR Dashboard |
| Data Web-services Annual Users:15,000 |
Research-derived, simulated, translational and clinical data archives. Dashboard for mashing multi-source socioeconomic and medical datasets, big data analytics, graphical data exploration and discovery | UMich
SOCR Data UCLA SOCR Data Archive SOCR Dashboard |
| Computational Infrastructure Annual Users:400,000 |
Comprehensive collection of web-tools for demonstrating probability, statistics, mathematics and engineering concepts. These include probability calculators, statistics analysis tools, data modeling and visualization, virtual games, simulations and experiments | UMich SOCR
Services Probability Distributome Resource SOCR Tables and high-precision calculators SOCR GitHub Source Code SOCR JIRA/Atlassian PM System SOCR GoogleCode SVN |
| Analysis Tools Annual Users:8,000 |
Modern HTML5 resources for exploratory analytics, data discovery, simulation, and visualization | SOCR HTML5
Webapps SOCR XTK BrainViewer |
| Learning Resources Annual Users:1,800,000 |
Community-built, open-access and multilingual resources blending information technology, scientific techniques and modern pedagogical concepts | SOCR
Probability and Statistics EBook (UMich) SOCR Probability and Statistics EBook (UCLA) Scientific Methods for Health Sciences (EBook) Scientific Methods for Health Sciences (Courses) SOCR Wiki Service (UMich) SOCR Wiki Service (UCLA) |
Interactive Visualization
Dynamic iteractive visualization of multimodal imaging data is difficult. This project aims to develop new techniques and software tools for managing, processing and visualizaiton of multimodal imaging and meta-data (e.g., See the Web-based WebGL Brain Viewer.
Other Projects
- Project 1: We have developed the first fully
stochastic Functional & Anatomic Sub-Volume Probabilistic
Atlas (F&A SVPA) for the elderly and Alzheimer's Disease
(AD) patients. This atlas allows us early diagnosis, prognosis
and planning of treatment for AD subjects, based on data of
their blood perfusion and brain anatomy. (F&A
SVPA)
- Project 2:, deals with quantifying (numerically)
the neurological and topological differences and similarities
between pairs of (MRI, fMRI, PET, CT) brain scans. We were able
to design metrics on the space of Fractal/Wavelet Transforms of
signals, that help us make quantitative distinctions between
equivalent medical images, using their transforms. The
theoretical function estimation schemes we introduced have been
used to develop an algorithm and a computer implementation for
an automatic fast and robust approach to quantifying warp
performance. This software package is called "Wavelet Analysis
of Image Registration" (WAIR)
- In Project 3, we develop a new technique for
determining the statistically significant metabolic variations
in single/multi-subject human brain functional studies. The new
method, called Sub-Volume Thresholding (SVT),
models the difference images as "locally" stationary Gaussian
random fields. Thus adding more flexibility to the commonly used
"globally" stationary random approaches. Our model naturally
encounters a class of continuous functions we showed induces a
family of permissible covariance matrices (valid covariograms).
Using the SVT technique we are trying to identify local
perfusions and differences in groups of; left vs right hand
motor studies; amnesia vs memory-retrieval deficit AD
(Alzheimer's disease) patients; and groups of hallucinations vs
delusion patients. If we wish to compare two images and identify
corresponding anatomical features (or regions of activation, for
functional data) we need to use a "warping" technique to deform
one of the images to an image similar to the second one. This
brings up the question of "What kind of deformation should we
use?".
- In Project 4, we constructed a mathematical model
(based on Fractal and Wavelet Analyses) that helps classifying
warps and warping techniques.
- Segmentation of medical images is the topic of Project
5. Using the discrete dynamical system induced by our fractal
transform we designed a segmentation algorithm. The two major
goals in brain image segmentation are: Determining the regions
of high concentration of White Matter, Gray Matter and CSF
(Cerebral Spinal Fluid); and Reducing the data complexity and
dimensionality.
- Our models, and our metrics, turn out also to be useful
for image magnification.In Project 6, we compared the
current state-of-the-art (bilinear) Interpolation techniques for
image zoom in, to the novel Fractal magnification algorithms. We
were able to show that our model outperforms the interpolation
method in some aspects. Blowing up images using their fractal
transforms reveals more details (at lower resolution) and avoids
the smearing and blurring effects of the interpolation.
- Fractal-like transformations could be used for automatic
pattern recognition and feature extraction. Project 7
deals with a simple application of such techniques. We are able
to show that a decent pattern recognition algorithm could be
used for image registration and alignment - a very useful tool
for image comparison.
- My work in various Optimization projects includes
developing, implementing and testing algorithms for solving
min/max, linear/non-linear problems/systems/inequalities. Using
Subdivision Traversing and other topological algorithms we
introduce a class of simple, fast and robust algorithms for
function optimization. The
casting problem serves as a motivation in this project. When casting an airplane wing, for example, there are a number of input variables (like: Temperature, Pressure, Flow velocity, alloy proportions, etc.) and a list of output characteristics (like: Strength, Number of voids, etc.). The problem is to increase the strength of the wing, decrease the number of bubbles (voids) etc., without actually knowing the function connecting the two types of variables. Currently, this problem is approached by some sort of uniform (or random) selection of test points (input variables), conducting an experiment and observing the output. We have designed an algorithm, that solves an optimization problem to optimize the search for the "right" input based on the previously obtained functional values at prior test points.

